Reproductive toxicity
- Due to risk to the fetus, fingolimod is contraindicated during pregnancy and in women of childbearing potential not using effective contraception. Before initiation of treatment, women of childbearing potential must be informed of this risk to the fetus, must have a negative pregnancy test and must use effective contraception during treatment and for two months after treatment discontinuation1,2
- Prevalence of major congenital malformations (EUROCAT classification) in prospective pregnancies exposed to fingolimod is presented below
- The prevalence of major malformations in the Safety database is higher than in EUROCAT with no overlap in confidence intervals3,4,5,6
- The prevalence of congenital heart defects in both the safety database and GPR is higher than in the EUROCAT general population
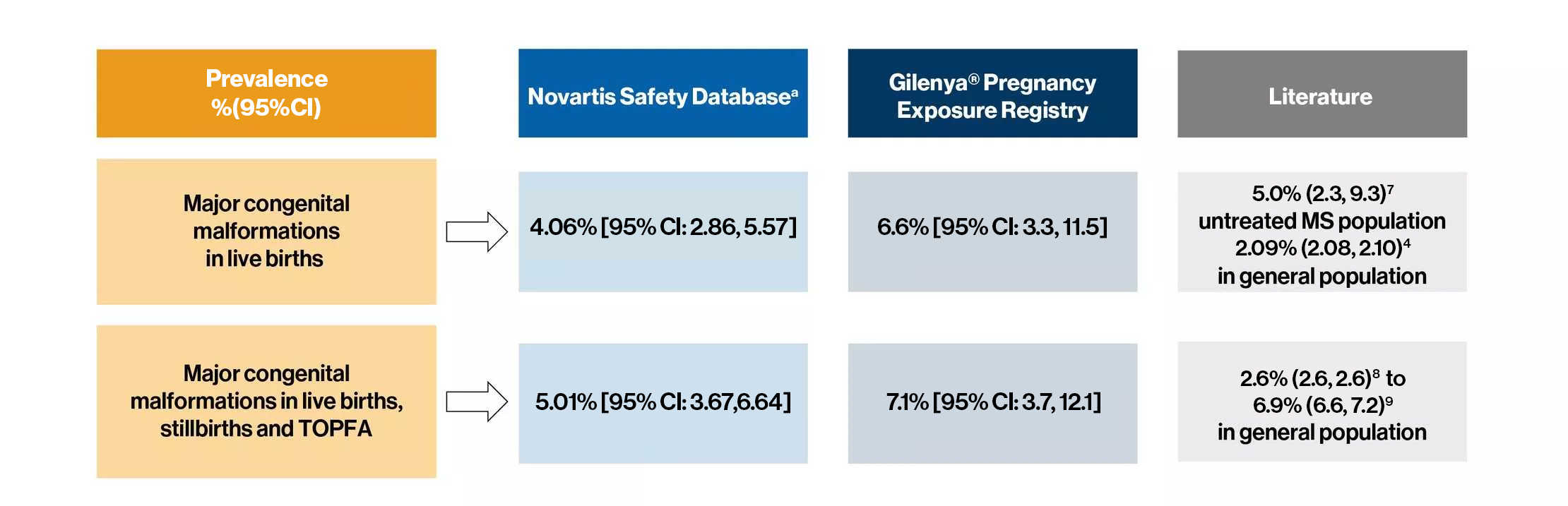
Major congenital malformations: Any structural defect with surgical, medical, or cosmetic importance recognized) are presented as a proportion of fetal cases in live births, or in live births, stillbirths, and termination of pregnancy due to fetal anomaly
a The denominator is all prospective pregnancies with known outcome. The prevalence is calculated as the number of fetuses/infants with at least one major malformation per 100 fetuses/infants. If any infants had multiple anomalies, only the worst anomaly was counted.
