PARADIGMS
Study design
Double-blind, randomized, active-controlled two-year study vs interferon beta-1a in pediatric patients with RRMS**
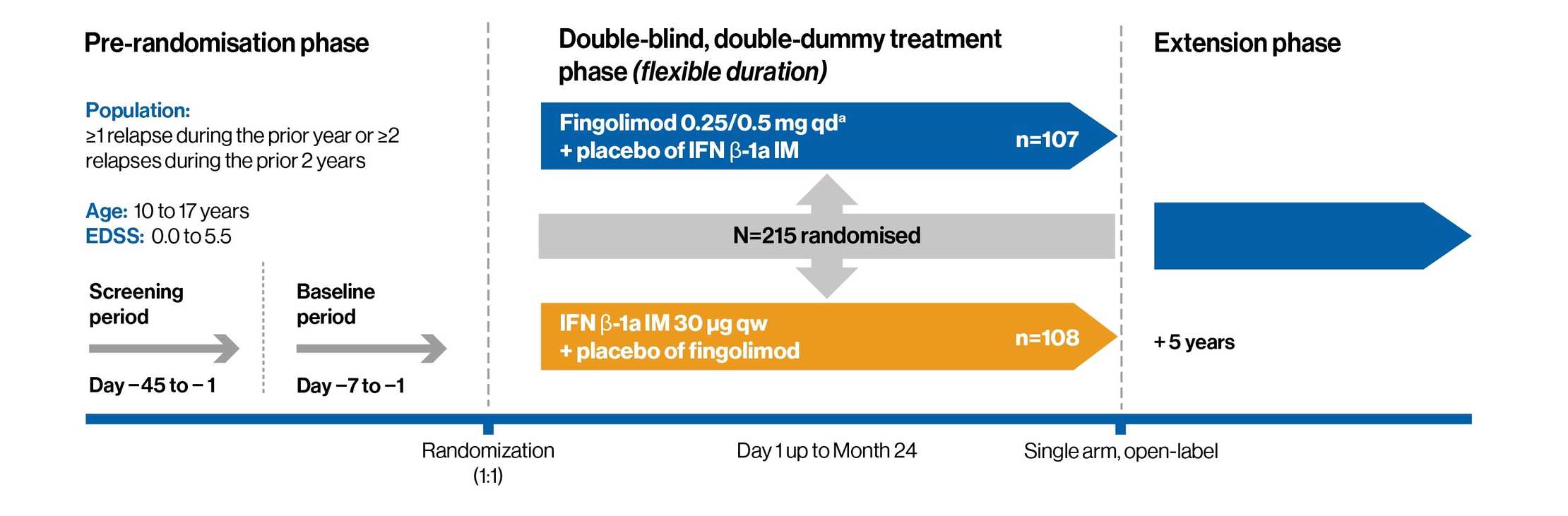
**Fingolimod has not been studied in children less than 10 years of age
A double-blind, randomized, clinical trial that compared the efficacy and safety of fingolimod 0.25 mg or 0.5 mg (dose selected based on body weight) once daily to intramuscular (IM) interferon beta-1a 30 mcg in 215 pediatric patients 10 to less than 18 years of age with RRMS
Patient baseline characteristics:
1. RRMS diagnosis based on the revised consensus definition for pediatric MS, which includes the 2010 McDonald criteria
2. EDSS score: 0-5.5. Median score at baseline was 1.5
3. Previously treated or treatment-naïve patients with at least 1 relapse in the past year, or 2 relapses in the previous 2 years, or evidence of at least 1 Gd+
T1 lesion on MRI in 6 months before randomization
4. No evidence of progressive MS or other immune system diseases or other demyelinating disorders, acute disseminated encephalomyelitis,
or neuromyelitis optica
Primary end point: The annualized relapse rate, defined as the average number of confirmed relapses per year over the period of active treatment
Key secondary end point: The annualized rate of new or newly enlarged lesions detected on T2-weighted MRI as compared with baseline
Other secondary end points:
1. Effect on Gd+ T1 lesions
2. Safety and tolerability
Patients were required to remain at the site for at least 6 hours after receiving the first dose of study drug (ie, first-dose monitoring on Day 1). First-dose observation included monitoring of vital signs (heart rate and blood pressure), for potential signs of bradycardia, and electrocardiography
Prior therapy with interferon-beta, dimethyl fumarate, or glatiramer acetate up to the time of randomization was permitted
Baseline assessments and neurologic evaluations were performed at screening. Additional neurological evaluations were completed every 3 months and at the time of suspected relapses
MRI evaluations were performed at screening, and every 6 months throughout the study
**Fingolimod has not been studied in children less than 10 years of age
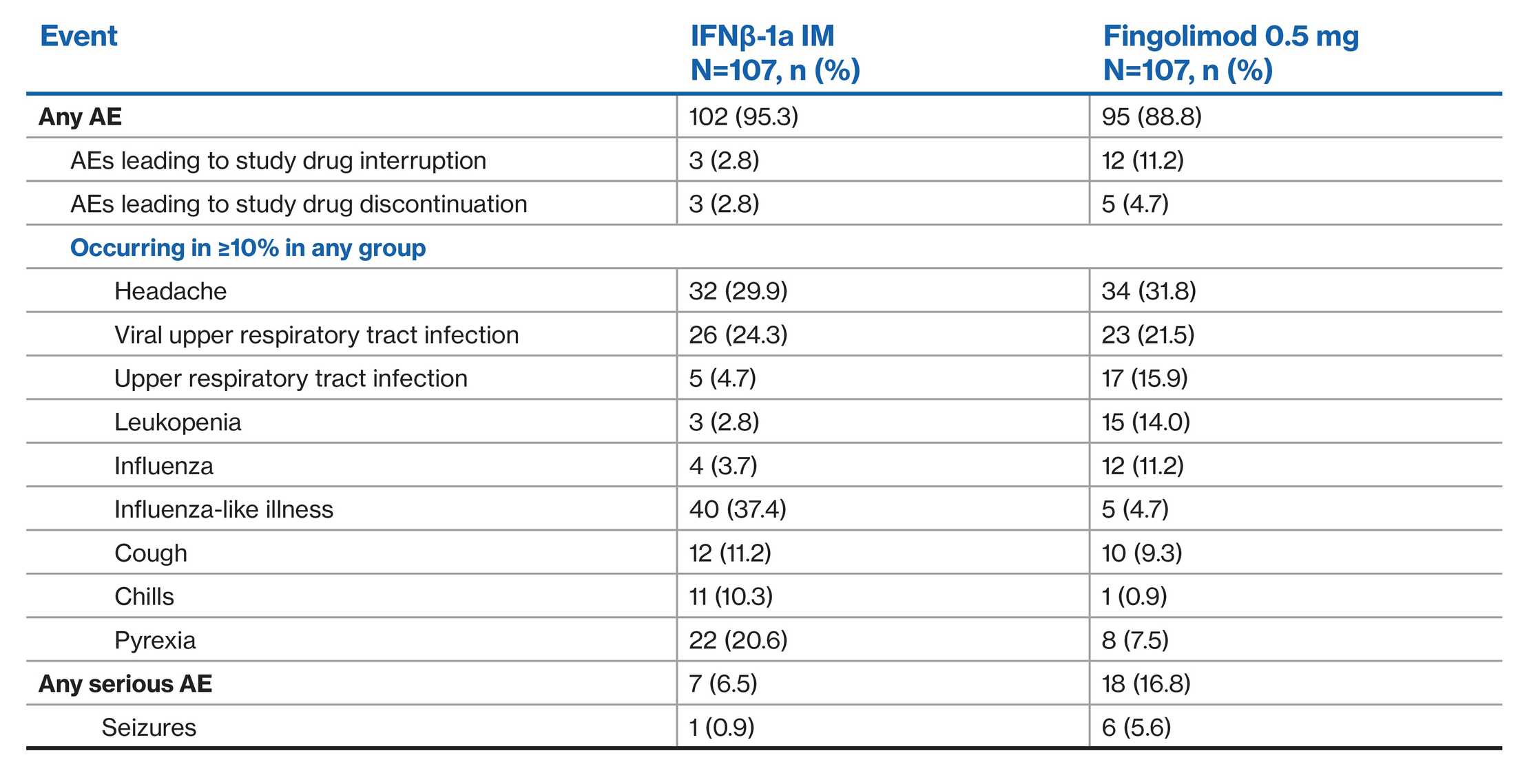
AE profile of fingolimod versus interferon: PARADIGMS double-blind treatment phase1
AE profile of fingolimod over 4.7 years: PARADIGMS extension study (Interim analysis)2
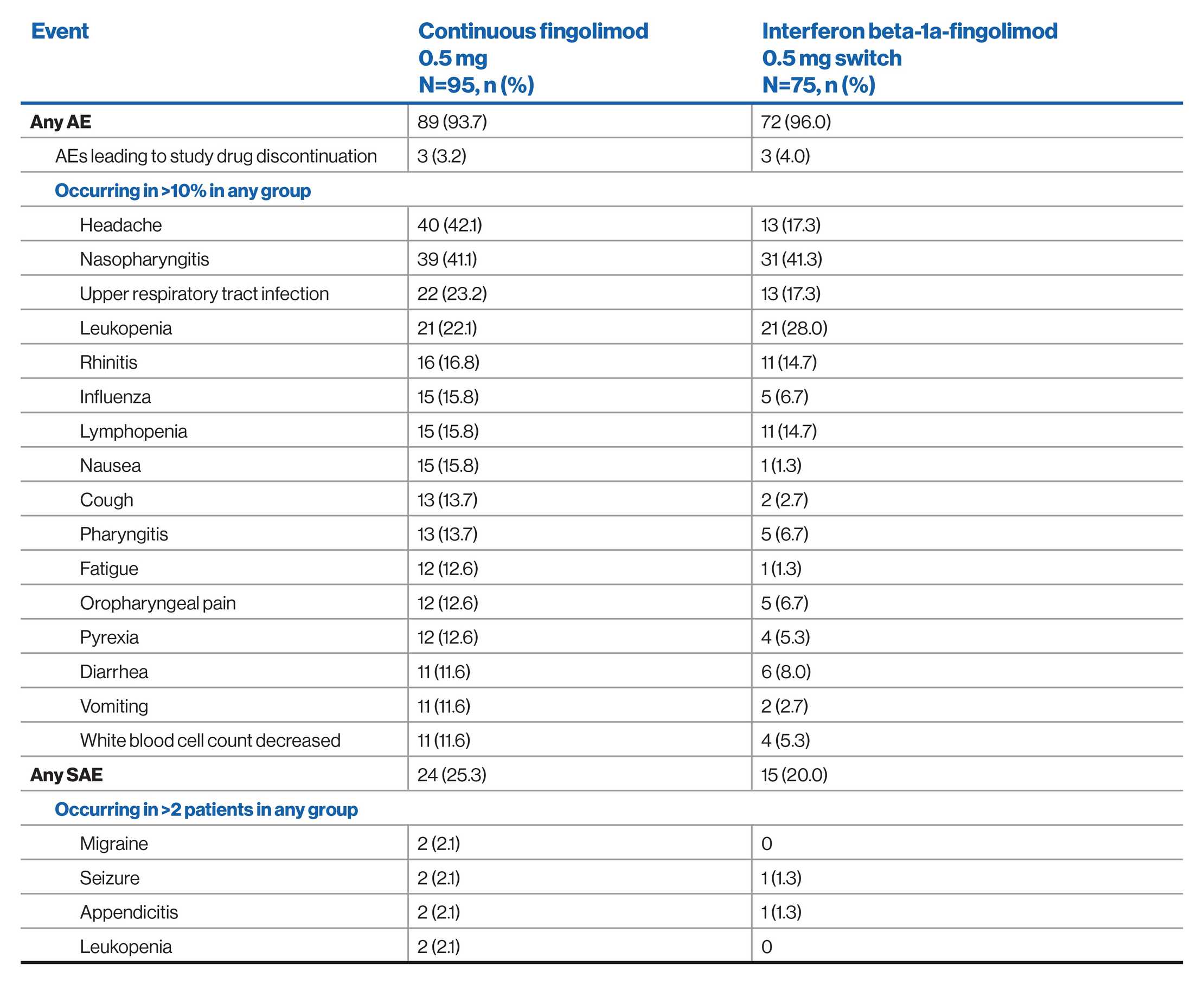
NOTE: Due to the interim nature of the analysis the data shown is subject to changes until the final data base lock.
