COVID-19
Last updated: February 2021. The page will be updated quarterly
It looks like you are using an older version of Internet Explorer which is not supported. We advise that you update your browser to the latest version of Microsoft Edge, or consider using other browsers such as Chrome, Firefox or Safari.
Last updated: February 2021. The page will be updated quarterly
Fingolimod and COVID-19Guidance to HCPs
SARS-CoV-2 vaccination considerations
|
Based on the totality of the data available from the COVID-19 case reports in the post-marketing setting and comprehensive data analysis by the MS Data Alliance Global Data sharing initiative9
Postmarketing
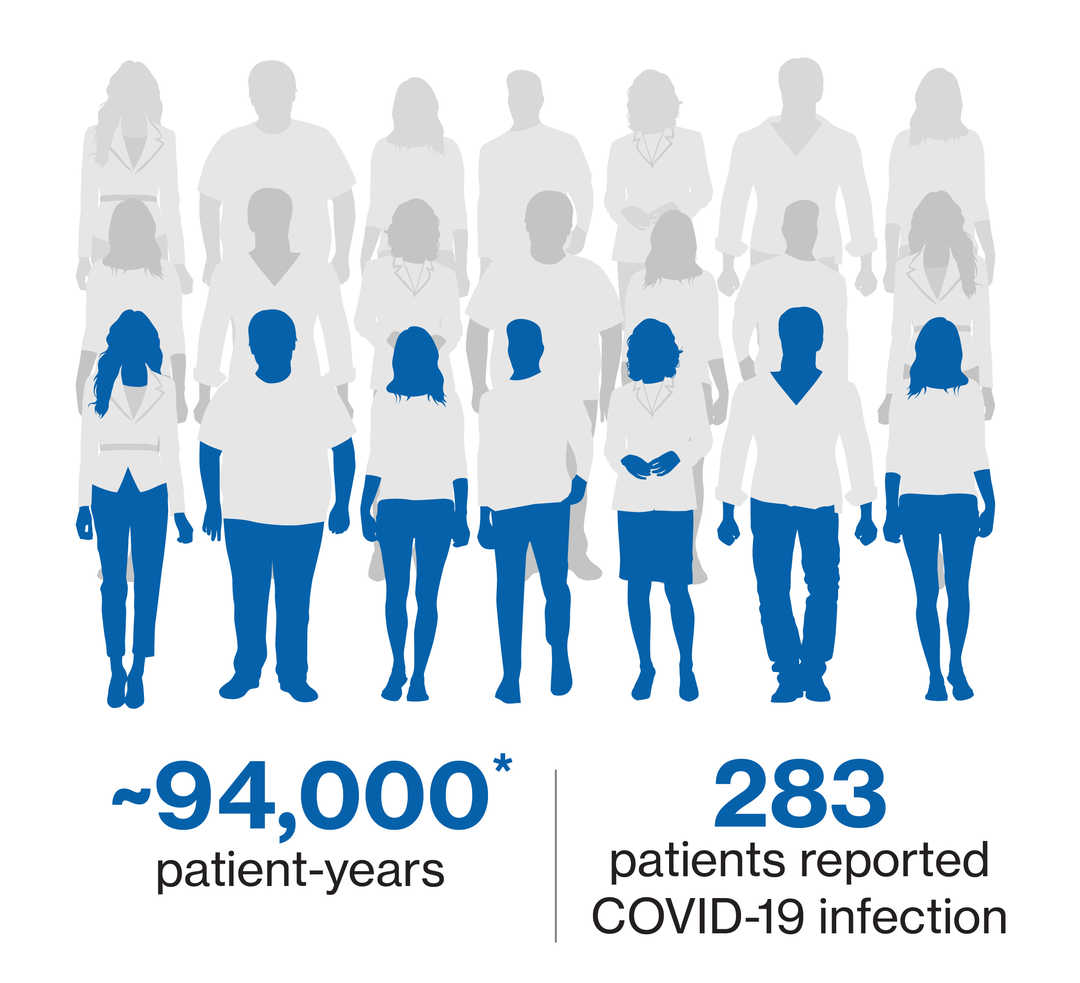
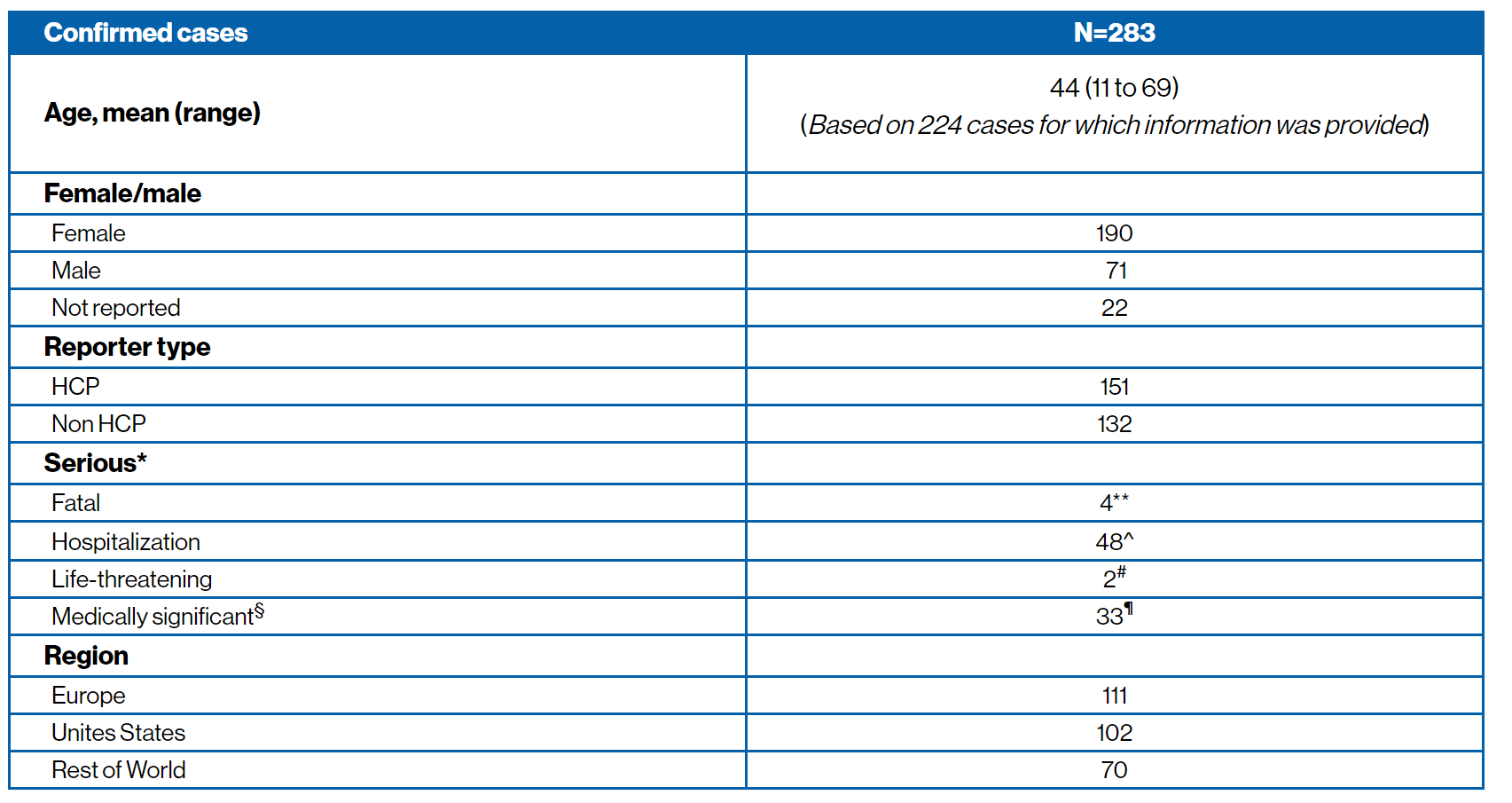
COVID-19 infection confirmed cases5
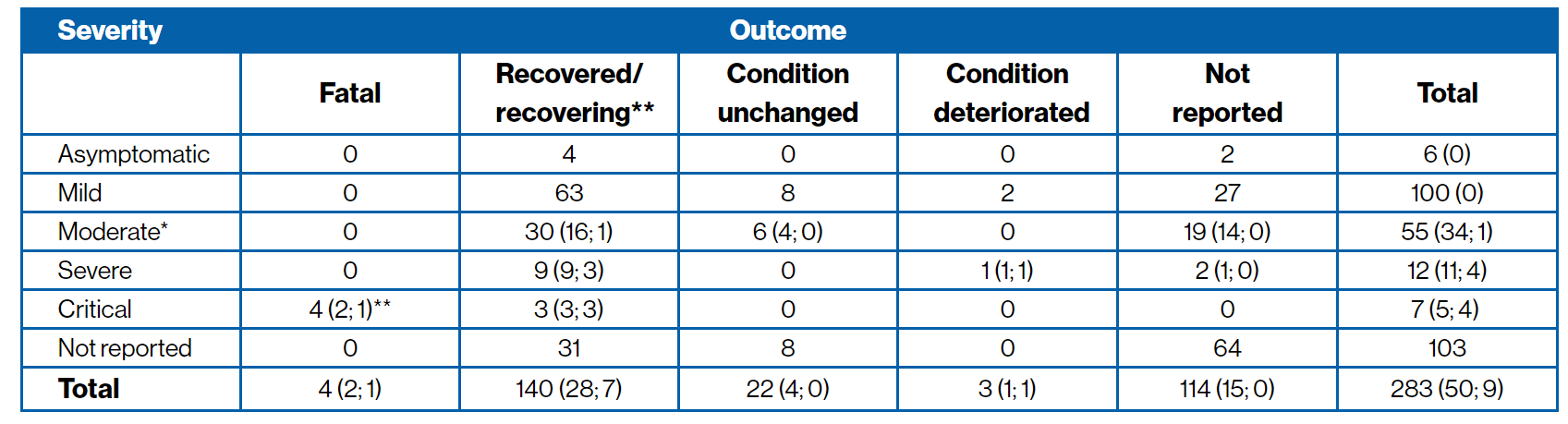
COVID-19 severity and outcome5
Impact of COVID-19 in MS in a real world setting

This website is for non-promotional purposes and is intended for providing
safety information for healthcare professionals (HCP) only
Please confirm that you are an HCP
For HCPs: Information on this website is not country specific, and may contain information that is outside the approved indications in the country in which you are located. Please contact your local Novartis representative for the latest information specific to your country.
For non-HCPs / patients: This safety website is available for HCPs only